The
human ERYF1
gene (summary) NF-E1
DNA-binding protein GATA1,
locus Xp11.23
[§§; †] containing 2 'finger'
motifs referred to as ERYF1 of an erythroid-specific gene. The
cDNA for the human ERYF1 gene is almost identical to that of
chicken and mouse GATA1
gene consisting of 2 zinc finger' type motifs its activator
domain contains the binding sites for protein GATA1 and the CACCC
(HS2)^
region. FOG is specific to this complex corresponding cDNA and
interacts with element in the beta-globin IVS2 promoter
from hemoglobin protein
subunit promoters (alpha-chain gene‡,
gamma, epsilon^
and (embryonic), a switch from fetal to
adult haemoglobin -or- relative
to the T to C substitution of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH),
implications for fetal hemoglobin - HbF``)
distinct for erythroid
(INHBA)
and megakaryocyte differentiation, in vertabrate though, the N- and C-terminal
thirds of the human protein. Friend of
GATA-1, FOG1; ZFPM1, zinc finger protein region a coregulator of the
GATA1 associations facilitates a chromatin locus
control region-(LCR) modifying proximity
fetal to adult (gamma)
to beta
globin including the erythroid (EKLF
krüpple-like) factor DNAse1^ histone hypersensative site (HS)^
locus (LCR)
GATA1 establishes, facilitates interactions with
immunoprecipitation, cross-regulatory roles reduced
histone, acetylation and antagonism (EKLF-FlI-1)
mechanisms. PU.1
- of the Ets family is 'synergistic' to the major basic
protein, (MBP)
handles bistability
in the erythroid-'myeloid
switch « directed by PU.1,'
influenced DNA
binding and is involved with MZF-1
(myeloid zinc finger 1), it interacts with the 'C-terminal
zinc finger « (CF)' of GATA1. A bipotential
function in multiple contexts (erythroid
versus megakaryocytic
myeloid cells, GATA1 switches myeloid cell fate into eosinophils)° as two multi-protein complexes
when segregated into two types (factor P-TEFb)
one of the
characteristics of (TAL-1,
T-cell
acute-) leukemic (SCL) stem
cells is both types in circulating blood, for both the
downregulation of GATA-1 and with the upregulation of GATA-2 (3q21)°
that CD34␠
has the transcription
capacity observed
in immature
hematopoietic
progenitor stem
cells, specific regions of each (Sequencing of FOG1
with GATA1
and GATA2),
requires intact DNA-binding
domains. The C-terminal zinc finger (CF) basic tail shares,
in an antagonistic fashion 'mutations' in
exon
2‡
(-GATA1s
is a shorter
GATA1 isoform (sf)
found in DS
(Down syndrome) a transient leukemia (TL)-AMKL)
that lacks the transactivation'"
domain, in cis-acting GATA element,
identification
requires intact long forms (lf) of NF-E1 DNA-binding domain.
Two novel zinc-finger domains
demonstrate that the NFE1 gene
cDNA-binding protein is assigned the human locus located in
Xp11.23, required for normal megakaryocytic and erythroid
development. A mutation in the FOG1-GATA1 N-terminal zinc
finger (N-finger of leukemic cell (Igs)-immunoglobulins)
or lacking the N-terminal activation
the binding of Fog1 and the N-finger in the DNA face
of Fog1, with non X-linked associations (16q22-24)
if different clinical entities linking to X-linked
(X is any amino acid, substitution in the DNA-binding (Nf) region) thrombocytopenia in males-(XLTT*'-GATA1)
with anemia
low platelet levels traces discernable steps as embryos
with a defect
in forming erythroid burst-forming units BFU-E
☞ (summary - of all DNA that is transcribed which occurred
at a exome
splice site), to Minimal residual disease MRD
- (cancer, "preleukemia" - myeloproliferative disorder (TMD),
myeloid
leukaemia-AML,
SCL°
and megakaryocytic AMKL)
the GATA1-HS2-modified
vector allowed remission in blood component and heme
(Protoporphyrinogen) at the seventh
GATA site in exon
1*'/intron-7°
as a cofactor involving 6 non-coding exons and transactivation
by USF1
and GATA1. A DNA Cytosine mechanism ara-c (Arabinofuranosylcytosine) short (sf)
and (lf) long forms is used to kill these megakaryocytic cancer
cells; clarifies that GATA-1
controls genes that manipulate the cell cycle and apoptotic
cell death underlying normal
(PI3K) and pathologic
(PU.1) erythropoiesis - 'differentiation' is (FKBP12) lacking basal
expression'" in contrast to Bcl
when Bcl-X(L) is cleaved by caspases. Anti-apoptotic Hsp70
protects GATA-1 during the switchingª
of the erythroleukemia␠
cells that fail to complete maturation, proteolysis undergoing cell death in both
the megakaryocytic
and erythroid
cells, established that phospholipase C (PLC)ª
is involved in the signalling pathway (PI3K)/Akt
equally expressed 'as' a probable
negative FOG
regulator, interacts with the PU.1
related Ets
domain of glycoprotein (GP)(1)
VI*' by expressing thrombopoietin activation of
platelets in megakaryocytic cell lines, expressing both Fli-1 and GATA-1. A weak loss of aspartate in the
amino-N-terminal zinc finger (Nf) loop GATA1's three base
substitution mutations
results in incomplete
megakaryocyte/platelet maturation as assessed by the DNA
demethylating agent 5-azacytidine, activity in
the presence of ara-c
which occurred at a
exome splice site. GATA1 appears
to interact with RNA-mediated basal expression against these
pathways, associated protein or mammalian targets clarified that the basal
transcription apparatus with transcription
factors`` appears to interact with an HS2 region mutated
in its GATA motif -GATA1s
a shorter
GATA1 isoform.
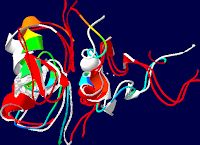
![sequence [AT]GATA[AG] upper left](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjNLGrxGiob2X55EpjU3v2vy3VU76ltNQx_JA6Tjwk9CTThRHMNfYcGp326ogIPzjdwCmMKGUXZSmJi6e9KMdMDmzOLdXvgL9fQqulKnzmo16XgJdhWcezIP2_decFRqLEtUxTrag/s200/1yoj-a-3vd6.png) |
 |
| Figure 1: PDB 1y0j-a (MMDB ID: 31470; Mus musculus A). superimpos |
Figure 2: 4 Angstroms of PDB
1GAT in this 4 Angstrom PDB 3VD6 rendering of 1YOJ-A RNA, modifyed to
complete Fig.1. both are manually defined selected to provide The two
zinc fingers functional |
 |
|
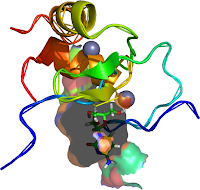
| Figure 3: This incorporat |
Zinc fingers as protein recognition motifs: structural basis for the GATA-1/Friend of GATA interaction
Rendered with Swiss PDB-viewer SPDBV about a horizontal axis of the Structures Image in the plane of the page http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?pdbId=1Y0J Refernce: Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(4):1215-27. GATA1 function, a paradigm for transcription factors in hematopoiesis. PMID: 15684376 Swiss-pdb viewer software (http://www.expasy.org/spdbv/) |
No comments:
Post a Comment