Glutathione peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.9) protects against oxidative
damage via the chemoprotective
action of nitric-oxide mediated lipid peroxidation and anti
oxidative defense by gluathione (GSH-Px1-GPX1)
a extracellular selenoenzyme, extracellular glutathione peroxidase (E-GPx) and
cellular (C-GPx)
detoxifies hydroperoxides. Other antioxidant genes (AOX) as Gpx1, is
located in the cytosol and
in (mt)
mitochondria. Epithelial antioxidative enzymes (AOEs) are
activities of GSH-Px1 (gluathione peroxidase), (SOD) superoxide
dismutase, and thioredoxine reductase (TXNRD1) by
itself or with thioredoxin (Trx) are
antioxidant enzymes. Glutaredoxin (Grx) are
reduced by the oxidation of glutathione an antioxidant, (The effect
of iridoid
 glucosides such as oleuropein an antioxidant, can often be
bound to glucose.) phenolic compound isothiocyanate
sulforaphane found in olive leaf, increased cell-lysate NAD(P)H:quinone
oxidoreductase (NQO1) phase
II activities reduction reactions, catalyzed such as by glutathione-S-transferase (GST) can catalyze the conjugation back
to the thiol
group and other GPx mimics (converted into selenocysteine),
to the reaction site of glutathione (GSH) and antioxidants,
implying (GR) reduction
reactions back to glutathione, are an evolutionary
relationship between GST and GPx/glutathione
system
defense in oxidative stress. "Glutathione" peroxidase (Gpx) content,
and glutathione reductase (GR) components compose the glutathione
(GSH) system, this contains Selenocysteine (Sec), the 21st amino
acid at the active GPX site (Homo sapiens chromosome 3, GRCh37
primary reference: rs644261)-
TGA
=> UGA
(selenocysteine,
which occurs at the active
site of glutathione peroxidase GPX1 is coded by UGA, isoform
1 NM_201397.1-variant
1 represents the shorter transcript that encodes the
longer isoform 1, as compared to isoform
2- NM_000581.2 variant
2); (rs1050450)
is intronless and has a shorter C-terminus. They represent the cDNA as a
molecular
mechanism (TGA)
for down-regulation
of mRNA expression
and transcriptional
code is a regulatory switch at
the translational-step
delivered to the ribosome in
genes similar to Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GP, Gpx1,
GSHPX1): locus 3p13-q12 (§, ‡,).
GSH-Px is an essential
nutrient selenium
dependent
GPX, by which mRNA translational repression of
selenium-binding protein (SBP1) is
accomplished when GPX1 increased in human plasma, if
selenium-deficient,
while independent of Se values in
leukocyte
(White blood cells) from correspondingly
damaged DNA.
In fibroblast
activity, GPx1
was effective
through the prevention
or repair
of DNA damage.
The reductive detoxification
of peroxides in cells modulates
xenobiotic metabolising enzymes via anticarcinogen supplementation,
e.g. selenium-yeast
 in human plasma.
GPX in turn,
can lead to carcinogenesis.
The heterozygote has an intraerythrocytic environment
(red blood cell) with the favorable higher peroxidase
activities role in malarial
resistance. An in-frame GCG
trinucleotide repeat was homozygous
for the pseudogene
GPX1 Pro197Leu-like two alleles associated with 6 GCG repeats coding for a polyalanine
tract. CuZn-SOD (copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase) and other oxidoreductases
contribute to the cellular defenses, repair of oxidative damage to
DNA. Chronic hyperglycemia
(excessive blood sugar) causes oxidative stress, 'Extract silymarin
and Berberine-'may'
overcome insulin resistance. And for diabetes Astragalus
membranaceus  can improve the protective effect, an extract
from Shidagonglao
roots (Mahonia fortunei)  or the effects of Berberine from the main
alkaloid of Coptis
chinensis  are agents for preventing sepsis and its
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
complications in human microvascular endothelial cells. GPX is
down-regulated and peroxiredoxin
(PRX) is up-regulated. Both use thioredoxin
(Gpx and
Prx, suppress Trx,
a cysteine-based thioredoxin-specific GPx-Txn expression.) to recharge after reducing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
along with other cellular
molecules. Also found in transcripts in ocular
tissues from oxidative
anterior damaged cells, GSH-dependent recombinant human lens thioltransferase
(RHLT)*
being its repair systems. GPX1 could supress staurosporine-induced
late generation of ROS, corresponding to reduction in visual
loss. Its role in pathogenesis of (inflammatory
disorders of blood antioxidant enzyme system)
as an autoimmune disease background, appears to be the hydroperoxide
metabolism in diverse pathogens*, an enzyme by single administration streptozotocin
 (60 mg/kg) of negative implication, oxidative damage or
antioxidant status when examined in contrast
as metabolic syndrome through the GPX down-regulation
are comparable, with reduced-enzyme-activity
to the T
allele of the GPx-1 genetic leucine/proline
polymorphism at codon 198
approximately 70% for pro197
and 30% for leu197
named Pro198Leu
(rs1050450).
The leucine-containing
allele was
less
responsive to GPx-1 enzyme
activity. Thioltransferase (TTase) with
GPx the dethiolating enzyme, thiol*
catalysis glutaredoxin thioltransferase (Grx)
content and activity to the thiol status produced by the oxidation
of glutathione:
a seleno-organic compound ebselen
(2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one) catalyzed in vitro, has
been reported to '« mimic »
development of small-molecule selenium compounds' ('synthetic
antioxidant' GPX) required for, a diphenyl diselenide PhSe group
'in the catalytic
activities' is introduced by reaction (a monocyte-derived soluble
protein (M-DSP/Gpx1)
with 5-LO,
(5-lipoxygenase ) activity this 'recovered
(M-DSP)-GPx inactivation'. In which Serum Malondialdehyde
(MDA) a marker
(oxidative activity) generated from, reactive oxygen species (ROS) is thought to
cause DNA damage with various antioxidants usually homeostatically
controlled by endogenous
superoxide dismutase (SOD), as a
by-product and the oxygen-sensor neuroglobin (Nb), GSHPx
reactive
neurons or in brief neuronal damage (apoptosis)
after ischemia.
Antioxidant enzymes such as Cu/Zn-superoxide
dismutase (SOD)
and a 21-kD
protein (involved in neuroprotection) GPx1 both in the free radical chain, protects neurons and Microglial
cells. Microglial cells are, sensitive to small changes from
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), free radical scavenging enzymes-mediated
apoptosis. Neuronal loss and deteriorating CNS
function: is linked to the pentose phosphate shunt, the (PPP)
pentose phosphate pathway, has a relatively low content of enzymatic
antioxidants, in a higher cellular ROS level
to oxidative stress. A candidate (SePP1) selenoprotein (P-plasma)
or genetic variations homologous to GPX1 are rapidly degraded at relative low selenium concentrations. Microsomal (reconstituted fraction) glutathione transferase-1 (hGSTP1)
decreased cytotoxicity ( cartilage degradation
and regeneration
[Leucas aspera] to mitochondria damage, directed to citrulline- containing proteins) by effects of hydrogen
peroxide 'H(2)O(2), which causes lipid peroxidation (LPO) in the (ER) endoplasmic reticulum. In
which LPO product Malondialdehyde and other Thiobarbituric acid reactive
substances - TBARS - are formed as a byproduct, when the effects of
GPX1 (
glutathione peroxidase 1)' is measured, the effects of Centella
asiatica  extract detoxifies. Antioxidants and detoxication
agents as antigenotoxic*
agents (isoflavones
via dietary
intake) were also observed as cytogenetic end-points* of
carcinogenesis. Over-expression could drain
the reduced
glutathione ( hepatic and GSH dependent enzymes), cellular
glutathione (GSH) levels, GSH acts as a feedback rate-limiting inhibitor of its synthesizing enzyme
GCL
(gamma-glutamyl-cysteine
synthetase) activity, Diosgenin 
is a useful Marker degradation-compound of Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and
high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
against oxidation. The compound buthionine
sulfoximine (BSO) inhibits the first step of glutathione
synthesis, concerning the mechanism of GSH depletion. Gpx suppresses (thioredoxin) Trx - expression, which augments Anti-clastogenic (mutagenic agents), potential DNA-binding (heritable multigenerational/evolutionary tolerance), in a cDNA open reading frame (ORF) GPx1 is a small inversion (~pericentric), incorporating the co-translational selenocysteine which may be unique to the insertion sequence
elements.
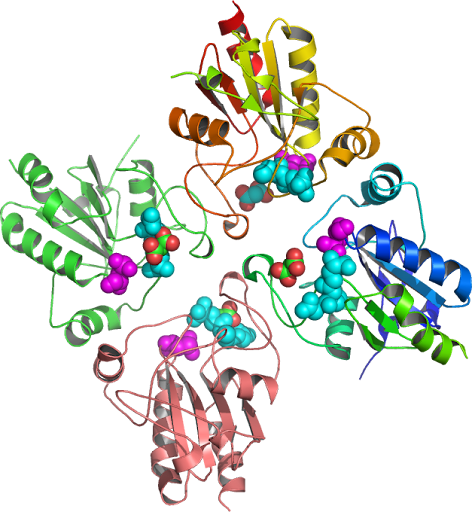 Biological Assembly GPx-1 tetrameric structure with an altered carcinogen metabolism and reduce oxygen tension to explain the anti-carcinogenic effects, the redox donor (hTXN-oxidoreductase Figure 4) status (Figure 2) of one oxygen
atom limited to only two regions may carry missense variant (rasmol_php_C and _D) a reaction
incorporated into the overall tetrameric structures instability
potentially in humans through modulation of biosynthetic and genetically
modified GSH enzymes binding the selenocysteine insertion sequence
elements. The
specific activity of the enzyme Sec suggest how the molecular
pathway might work, as the glutathione pathway may influence the
enzyme Sec reaction site incorporation sequence in the
3'-untranslated region UTR of
glutathione (GSH) may further reveal a signaling pathway that is
activated. The differing and interacting roles of GPX1 and (Sec.) Selenocysteine
Synthase [doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_8] both vectors
Biological Assembly GPx-1 tetrameric structure with an altered carcinogen metabolism and reduce oxygen tension to explain the anti-carcinogenic effects, the redox donor (hTXN-oxidoreductase Figure 4) status (Figure 2) of one oxygen
atom limited to only two regions may carry missense variant (rasmol_php_C and _D) a reaction
incorporated into the overall tetrameric structures instability
potentially in humans through modulation of biosynthetic and genetically
modified GSH enzymes binding the selenocysteine insertion sequence
elements. The
specific activity of the enzyme Sec suggest how the molecular
pathway might work, as the glutathione pathway may influence the
enzyme Sec reaction site incorporation sequence in the
3'-untranslated region UTR of
glutathione (GSH) may further reveal a signaling pathway that is
activated. The differing and interacting roles of GPX1 and (Sec.) Selenocysteine
Synthase [doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_8] both vectors together with glutathione (HUMAN GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE (HGST) PDB
ID: 1LJR
ligand component
GSH: C10 H17 N3 O6 S, molecules colored: aquamarine) did; activates two multiple signaling
pathways in one of the Gpx1 variants 1 or 2 nucleotide, the nonsense
codon, UGA has both, related to the antioxidative pathway vectors
together PDB ID: 1gp1
(2-AMINO-3-SELENINO-PROPIONIC ACID: ALANINE molecule colored: purple),
is located near the selenocysteine insertion sequence element PDB
ID: 2F8A (rainbow colored: ribbons) mutant of GPX1. Interrogation of data based on
experimentally determined models are limited but revealed network
structures that dynamically conveyed information from the
antioxidant enzymes that share a common pathway considered most
important in the selenocysteine synthesis pathway from the
information suggested, and they implicate at least one selenoprotein (GPx-1) in the process.
together with glutathione (HUMAN GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE (HGST) PDB
ID: 1LJR
ligand component
GSH: C10 H17 N3 O6 S, molecules colored: aquamarine) did; activates two multiple signaling
pathways in one of the Gpx1 variants 1 or 2 nucleotide, the nonsense
codon, UGA has both, related to the antioxidative pathway vectors
together PDB ID: 1gp1
(2-AMINO-3-SELENINO-PROPIONIC ACID: ALANINE molecule colored: purple),
is located near the selenocysteine insertion sequence element PDB
ID: 2F8A (rainbow colored: ribbons) mutant of GPX1. Interrogation of data based on
experimentally determined models are limited but revealed network
structures that dynamically conveyed information from the
antioxidant enzymes that share a common pathway considered most
important in the selenocysteine synthesis pathway from the
information suggested, and they implicate at least one selenoprotein (GPx-1) in the process.
(Click on image to zoom)
 Biological Assembly GPx-1 tetrameric structure with an altered carcinogen metabolism and reduce oxygen tension to explain the anti-carcinogenic effects, the redox donor (hTXN-oxidoreductase Figure 4) status (Figure 2) of one oxygen
atom limited to only two regions may carry missense variant (rasmol_php_C and _D) a reaction
incorporated into the overall tetrameric structures instability
potentially in humans through modulation of biosynthetic and genetically
modified GSH enzymes binding the selenocysteine insertion sequence
elements. The
specific activity of the enzyme Sec suggest how the molecular
pathway might work, as the glutathione pathway may influence the
enzyme Sec reaction site incorporation sequence in the
3'-untranslated region UTR of
glutathione (GSH) may further reveal a signaling pathway that is
activated. The differing and interacting roles of GPX1 and (Sec.) Selenocysteine
Synthase [doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_8] both vectors
Biological Assembly GPx-1 tetrameric structure with an altered carcinogen metabolism and reduce oxygen tension to explain the anti-carcinogenic effects, the redox donor (hTXN-oxidoreductase Figure 4) status (Figure 2) of one oxygen
atom limited to only two regions may carry missense variant (rasmol_php_C and _D) a reaction
incorporated into the overall tetrameric structures instability
potentially in humans through modulation of biosynthetic and genetically
modified GSH enzymes binding the selenocysteine insertion sequence
elements. The
specific activity of the enzyme Sec suggest how the molecular
pathway might work, as the glutathione pathway may influence the
enzyme Sec reaction site incorporation sequence in the
3'-untranslated region UTR of
glutathione (GSH) may further reveal a signaling pathway that is
activated. The differing and interacting roles of GPX1 and (Sec.) Selenocysteine
Synthase [doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_8] both vectors together with glutathione (HUMAN GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE (HGST) PDB
ID: 1LJR
ligand component
GSH: C10 H17 N3 O6 S, molecules colored: aquamarine) did; activates two multiple signaling
pathways in one of the Gpx1 variants 1 or 2 nucleotide, the nonsense
codon, UGA has both, related to the antioxidative pathway vectors
together PDB ID: 1gp1
(2-AMINO-3-SELENINO-PROPIONIC ACID: ALANINE molecule colored: purple),
is located near the selenocysteine insertion sequence element PDB
ID: 2F8A (rainbow colored: ribbons) mutant of GPX1. Interrogation of data based on
experimentally determined models are limited but revealed network
structures that dynamically conveyed information from the
antioxidant enzymes that share a common pathway considered most
important in the selenocysteine synthesis pathway from the
information suggested, and they implicate at least one selenoprotein (GPx-1) in the process.
together with glutathione (HUMAN GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE (HGST) PDB
ID: 1LJR
ligand component
GSH: C10 H17 N3 O6 S, molecules colored: aquamarine) did; activates two multiple signaling
pathways in one of the Gpx1 variants 1 or 2 nucleotide, the nonsense
codon, UGA has both, related to the antioxidative pathway vectors
together PDB ID: 1gp1
(2-AMINO-3-SELENINO-PROPIONIC ACID: ALANINE molecule colored: purple),
is located near the selenocysteine insertion sequence element PDB
ID: 2F8A (rainbow colored: ribbons) mutant of GPX1. Interrogation of data based on
experimentally determined models are limited but revealed network
structures that dynamically conveyed information from the
antioxidant enzymes that share a common pathway considered most
important in the selenocysteine synthesis pathway from the
information suggested, and they implicate at least one selenoprotein (GPx-1) in the process.
No comments:
Post a Comment