Glutathione reductase (GSR, GR) locus in the chromosomal region
8p21.1, (EC 1.8.1.7)-(§,
‡)
is a protein-S-glutathionylation,
as a (human)
Mitochondrial
localization of hGSR and its associated enzymes cellular
thiol/disulfides S-Glutathione reductase (GSR) which is the
importance of significance in reversible
thiol modifications which regenerates reduced glutathione (GSH) and GSSG to the
reduced form found in the obvious
structural properties of glutathione reductase. The redox regulating
enzymes relationship with TTase (thioltransferase)
activity with the ratio of the activities of G3PD, as the mechanism
(of cellular repair) 'differs' (gssg-g6pg) according to the type of
reducing glutathionylated mixed disulfide, including
protein-S-S-glutathione (PSSG), GSR reduces
(PSSG) modified by thiolation
to a normal
level in human lens epithelial (HLE) cells. This may have implications
in stress- and aging-related
pathologies in astrocytes
and granule
cells, demonstrated
by comparable mitochondria/cytosolic
concentrations of its thiol proteins, where a mitochondrial leader
sequence (cDNA)
is present
in the gene structure of human GSR and may be the Cytoplasmic
Isoform (derivative or inhibitor formed) of mitochondrial dysfunction
that contains the catalytic
cysteine revealing a possible therapeutic strategy/target, also
indicating transiently accumulated inhibitor proteins modified by
thiolation (cysteine catalytic subunits) compounds that inhibit
these (re)activation processes (hGSR) with its structure-based prosthetic
group (FAD)
cofactor is common because of the levels of cysteine available; are
mitochondria/cytosolic concentrations that the Glutathione
reductases reversible thiol modifications which catalyzes the
reduction of GSSG to GSH the natural GR substrate
is dependent on the NADPH:GS-SG
ratio.
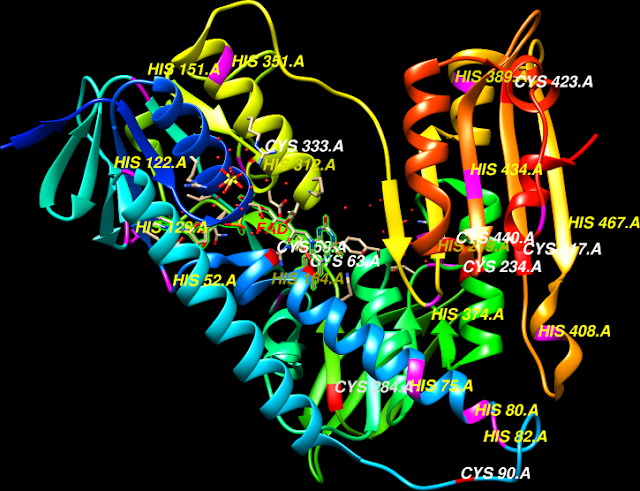 Cys58 and Cys63 represent the enzyme's results seen
as the reductive
(GSH) Cys-58 and oxidative
(GSSG) Cys-63
is the relationship of these two enzymes, His467' is seen
to interact with Cys63 more optimally and Cys-58 produces the second
GSH intermediate
molecule of the reaction is the reduced glutathione-to-oxidized
glutathione ratio (GSH/GS-SG)
when compared to the substrate free form correlated with (FAD) the flavin
compounds, flow from NADPH to the substrate GSSG via flavin.
The reducing
equivalents needed for regeneration of GSH are provided by NADPH. The
enzyme has affinity
for flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) the prosthetic
group of GR, and maintains high levels of reduced glutathione
(Cytoplasmic
Isoform: Produced by alternative
initiation of isoform Mitochondrial
homodimer, derivative
or inhibitor
formed from the GSR Pyridine, dimerisation
domain.) in the cytosol. Glutathione reductase (GR) plays a key role
in maintaining either a thiol group
or a nonprotein sulfhydryl
group (NPS)
form of GSH, and potential for thioredoxin
and glutathione systems, as thioredoxin
dose not require GSH and GR for
catalytic activity. Glutathione reductase (GR) utilizes
NADPH produced
by G6PDH
(glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) enzyme activities, and enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and inactivation in the activity of GSH peroxidase
and GSH
reductase. Expression of the regulatory subunit of
gamma-glutamylcysteine
synthetase/ligase (GCL)
catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the production
of the cellular (GSH) glutathione. Dietary riboflavin
(Vitamin B2)
intake produces its active essential coenzyme flavin forms,
riboflavin mononucleotide
(FMN) and
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) of
glutathione reductase (GR), or
the GR activity correlated
with red-cell flavin
compounds.When both GSSG and NADP(+)
substrates and products are present, glutathione reductase (GR) is a enzyme required for
the conversion in the presence and absence of flavin adenine
dinucleotide (FAD), glutathione reductase (GR) is an obligatory FAD-containing homodimer. GSSG via
glutathione reductase (GR) regenerates reduced glutathione which is
essential for antioxidant defense. The flavoenzyme glutathione
reductase (GR)
reduces 'oxidized glutathione' (GSSG) back to GSH, also involving
glutamate-cysteine ligase and modulatory
(GCL)-can
be upregulated ∉ as the cellular GSH system,
indicating short-term
and heritable
tolerance of exposure
to oxidative stress from/via numerous reporting ∈ mechanisms. NADPH is used by glutathione reductase for the reduction
of oxidized glutathione (glutathione disulphide) GSSG to
GSH-dependent peroxide metabolism. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one
of the major end
products of lipid
peroxidation which may lead to enhanced action of the (GSR) oxygen
radical, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are specifically suited
to the detoxification
and removal of 4-HNE (∋ or ∝) from cells which may provide a basis
for selective cellular and/or subcellular distribution of mitochondrial
and cytosolic to individual detoxifying gene inducer activities of glutathione reductase (GR), the cellular (GSH) glutathione. It was evident the enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and the (∉ or ∝) inhibition constant for reversible inactivation in the activity of glutathione related antioxidant enzymes. And GSH
reductase
may be one of the factors that remained in focus that suggests its
effects on the antioxidant system related to glutathione synthesis (GCL), degradation, and functions.
Cys58 and Cys63 represent the enzyme's results seen
as the reductive
(GSH) Cys-58 and oxidative
(GSSG) Cys-63
is the relationship of these two enzymes, His467' is seen
to interact with Cys63 more optimally and Cys-58 produces the second
GSH intermediate
molecule of the reaction is the reduced glutathione-to-oxidized
glutathione ratio (GSH/GS-SG)
when compared to the substrate free form correlated with (FAD) the flavin
compounds, flow from NADPH to the substrate GSSG via flavin.
The reducing
equivalents needed for regeneration of GSH are provided by NADPH. The
enzyme has affinity
for flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) the prosthetic
group of GR, and maintains high levels of reduced glutathione
(Cytoplasmic
Isoform: Produced by alternative
initiation of isoform Mitochondrial
homodimer, derivative
or inhibitor
formed from the GSR Pyridine, dimerisation
domain.) in the cytosol. Glutathione reductase (GR) plays a key role
in maintaining either a thiol group
or a nonprotein sulfhydryl
group (NPS)
form of GSH, and potential for thioredoxin
and glutathione systems, as thioredoxin
dose not require GSH and GR for
catalytic activity. Glutathione reductase (GR) utilizes
NADPH produced
by G6PDH
(glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) enzyme activities, and enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and inactivation in the activity of GSH peroxidase
and GSH
reductase. Expression of the regulatory subunit of
gamma-glutamylcysteine
synthetase/ligase (GCL)
catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the production
of the cellular (GSH) glutathione. Dietary riboflavin
(Vitamin B2)
intake produces its active essential coenzyme flavin forms,
riboflavin mononucleotide
(FMN) and
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) of
glutathione reductase (GR), or
the GR activity correlated
with red-cell flavin
compounds.When both GSSG and NADP(+)
substrates and products are present, glutathione reductase (GR) is a enzyme required for
the conversion in the presence and absence of flavin adenine
dinucleotide (FAD), glutathione reductase (GR) is an obligatory FAD-containing homodimer. GSSG via
glutathione reductase (GR) regenerates reduced glutathione which is
essential for antioxidant defense. The flavoenzyme glutathione
reductase (GR)
reduces 'oxidized glutathione' (GSSG) back to GSH, also involving
glutamate-cysteine ligase and modulatory
(GCL)-can
be upregulated ∉ as the cellular GSH system,
indicating short-term
and heritable
tolerance of exposure
to oxidative stress from/via numerous reporting ∈ mechanisms. NADPH is used by glutathione reductase for the reduction
of oxidized glutathione (glutathione disulphide) GSSG to
GSH-dependent peroxide metabolism. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one
of the major end
products of lipid
peroxidation which may lead to enhanced action of the (GSR) oxygen
radical, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are specifically suited
to the detoxification
and removal of 4-HNE (∋ or ∝) from cells which may provide a basis
for selective cellular and/or subcellular distribution of mitochondrial
and cytosolic to individual detoxifying gene inducer activities of glutathione reductase (GR), the cellular (GSH) glutathione. It was evident the enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and the (∉ or ∝) inhibition constant for reversible inactivation in the activity of glutathione related antioxidant enzymes. And GSH
reductase
may be one of the factors that remained in focus that suggests its
effects on the antioxidant system related to glutathione synthesis (GCL), degradation, and functions.
 Cys58 and Cys63 represent the enzyme's results seen
as the reductive
(GSH) Cys-58 and oxidative
(GSSG) Cys-63
is the relationship of these two enzymes, His467' is seen
to interact with Cys63 more optimally and Cys-58 produces the second
GSH intermediate
molecule of the reaction is the reduced glutathione-to-oxidized
glutathione ratio (GSH/GS-SG)
when compared to the substrate free form correlated with (FAD) the flavin
compounds, flow from NADPH to the substrate GSSG via flavin.
The reducing
equivalents needed for regeneration of GSH are provided by NADPH. The
enzyme has affinity
for flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) the prosthetic
group of GR, and maintains high levels of reduced glutathione
(Cytoplasmic
Isoform: Produced by alternative
initiation of isoform Mitochondrial
homodimer, derivative
or inhibitor
formed from the GSR Pyridine, dimerisation
domain.) in the cytosol. Glutathione reductase (GR) plays a key role
in maintaining either a thiol group
or a nonprotein sulfhydryl
group (NPS)
form of GSH, and potential for thioredoxin
and glutathione systems, as thioredoxin
dose not require GSH and GR for
catalytic activity. Glutathione reductase (GR) utilizes
NADPH produced
by G6PDH
(glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) enzyme activities, and enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and inactivation in the activity of GSH peroxidase
and GSH
reductase. Expression of the regulatory subunit of
gamma-glutamylcysteine
synthetase/ligase (GCL)
catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the production
of the cellular (GSH) glutathione. Dietary riboflavin
(Vitamin B2)
intake produces its active essential coenzyme flavin forms,
riboflavin mononucleotide
(FMN) and
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) of
glutathione reductase (GR), or
the GR activity correlated
with red-cell flavin
compounds.When both GSSG and NADP(+)
substrates and products are present, glutathione reductase (GR) is a enzyme required for
the conversion in the presence and absence of flavin adenine
dinucleotide (FAD), glutathione reductase (GR) is an obligatory FAD-containing homodimer. GSSG via
glutathione reductase (GR) regenerates reduced glutathione which is
essential for antioxidant defense. The flavoenzyme glutathione
reductase (GR)
reduces 'oxidized glutathione' (GSSG) back to GSH, also involving
glutamate-cysteine ligase and modulatory
(GCL)-can
be upregulated ∉ as the cellular GSH system,
indicating short-term
and heritable
tolerance of exposure
to oxidative stress from/via numerous reporting ∈ mechanisms. NADPH is used by glutathione reductase for the reduction
of oxidized glutathione (glutathione disulphide) GSSG to
GSH-dependent peroxide metabolism. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one
of the major end
products of lipid
peroxidation which may lead to enhanced action of the (GSR) oxygen
radical, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are specifically suited
to the detoxification
and removal of 4-HNE (∋ or ∝) from cells which may provide a basis
for selective cellular and/or subcellular distribution of mitochondrial
and cytosolic to individual detoxifying gene inducer activities of glutathione reductase (GR), the cellular (GSH) glutathione. It was evident the enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and the (∉ or ∝) inhibition constant for reversible inactivation in the activity of glutathione related antioxidant enzymes. And GSH
reductase
may be one of the factors that remained in focus that suggests its
effects on the antioxidant system related to glutathione synthesis (GCL), degradation, and functions.
Cys58 and Cys63 represent the enzyme's results seen
as the reductive
(GSH) Cys-58 and oxidative
(GSSG) Cys-63
is the relationship of these two enzymes, His467' is seen
to interact with Cys63 more optimally and Cys-58 produces the second
GSH intermediate
molecule of the reaction is the reduced glutathione-to-oxidized
glutathione ratio (GSH/GS-SG)
when compared to the substrate free form correlated with (FAD) the flavin
compounds, flow from NADPH to the substrate GSSG via flavin.
The reducing
equivalents needed for regeneration of GSH are provided by NADPH. The
enzyme has affinity
for flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) the prosthetic
group of GR, and maintains high levels of reduced glutathione
(Cytoplasmic
Isoform: Produced by alternative
initiation of isoform Mitochondrial
homodimer, derivative
or inhibitor
formed from the GSR Pyridine, dimerisation
domain.) in the cytosol. Glutathione reductase (GR) plays a key role
in maintaining either a thiol group
or a nonprotein sulfhydryl
group (NPS)
form of GSH, and potential for thioredoxin
and glutathione systems, as thioredoxin
dose not require GSH and GR for
catalytic activity. Glutathione reductase (GR) utilizes
NADPH produced
by G6PDH
(glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) enzyme activities, and enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and inactivation in the activity of GSH peroxidase
and GSH
reductase. Expression of the regulatory subunit of
gamma-glutamylcysteine
synthetase/ligase (GCL)
catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the production
of the cellular (GSH) glutathione. Dietary riboflavin
(Vitamin B2)
intake produces its active essential coenzyme flavin forms,
riboflavin mononucleotide
(FMN) and
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) of
glutathione reductase (GR), or
the GR activity correlated
with red-cell flavin
compounds.When both GSSG and NADP(+)
substrates and products are present, glutathione reductase (GR) is a enzyme required for
the conversion in the presence and absence of flavin adenine
dinucleotide (FAD), glutathione reductase (GR) is an obligatory FAD-containing homodimer. GSSG via
glutathione reductase (GR) regenerates reduced glutathione which is
essential for antioxidant defense. The flavoenzyme glutathione
reductase (GR)
reduces 'oxidized glutathione' (GSSG) back to GSH, also involving
glutamate-cysteine ligase and modulatory
(GCL)-can
be upregulated ∉ as the cellular GSH system,
indicating short-term
and heritable
tolerance of exposure
to oxidative stress from/via numerous reporting ∈ mechanisms. NADPH is used by glutathione reductase for the reduction
of oxidized glutathione (glutathione disulphide) GSSG to
GSH-dependent peroxide metabolism. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one
of the major end
products of lipid
peroxidation which may lead to enhanced action of the (GSR) oxygen
radical, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are specifically suited
to the detoxification
and removal of 4-HNE (∋ or ∝) from cells which may provide a basis
for selective cellular and/or subcellular distribution of mitochondrial
and cytosolic to individual detoxifying gene inducer activities of glutathione reductase (GR), the cellular (GSH) glutathione. It was evident the enzyme
glutathione reductase (GR) represents
the erythrocyte glutathione-reducing system (GRS), of the
GSH pathway to oxidation and the (∉ or ∝) inhibition constant for reversible inactivation in the activity of glutathione related antioxidant enzymes. And GSH
reductase
may be one of the factors that remained in focus that suggests its
effects on the antioxidant system related to glutathione synthesis (GCL), degradation, and functions.
Biological Xenobiotics, Extracts, Applications of note In the presence of Glutathione reductase.:
Schisandrin (Schisandra chinensis), used in traditional Chinese
medicine. PMID:21328628
Transketolase (TK) and transaldolase (TA)
Melatonin PMID:15571523, 19475625
Blackberry (Rubus sp.) cultivars, The 'Hull Thornless',
PMID:11087537
Glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate)-[dehydroascorbate reductase
(DHAR), and glutathione reductase (GR). This enzyme participates in
the glutathione metabolism the active metabolite of vitamin D3
increases glutathione levels.] PMID:11087537, 23770363
3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione nutraceutical D3T potently induces the
cellular GSH system, Anethole trithione is a drug used in the
treatment of dry mouth, the Anethole trithione isomer is related to
anethole (anise camphor) used as a flavoring substance.
PMID:17206382*, 19408115, 19176875*, 15896789,
18408143*, 

16946404*
Cassia fistula used in herbal medicine. PMID:19088944
Sanguinarine is extracted from some plants, including bloodroot and
Mexican prickly poppy (Argemone mexicana) where argimone oil causes
Epidemic dropsy. PMID:11260782
Vitamin E, PMID: 15672860
Tocotrienols are natural compounds members of the vitamin E family
found in select vegetable oils are an essential nutrient for the
body. PMID:21845802
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are produced by plants as a defense
mechanism against insect herbivores consumption of PAs is known as
pyrrolizidine alkaloidosis. PMID:20144959
Apple extract (AE) PMID:20401791
Lipoic Acid an organic compound, forming a disulfide bond, available
as a dietary supplement PMID:15246746, 21073761
Carnitine PMID:15246746, 10581232
Vitamin D upregulated expression of GCLC and GR. PMID:23770363
Vitamin D3_ PMID:12416023
Vitamin E_ PMID:10459841, 8360018, 18296478, 21845802, 15490422,
16885600, 7062348, 20729758, 21086752
Shidagonglao roots Mahonia fortunei (十大功劳 shi da gong lao) species
contains the alkaloid berberine PMID:199382 18
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) PMID:16621054
Trigonella foenum graecum seed powder (TSP) PMID:15026271
Boschniakia rossica, a ̱̱̱Traditional Chinese medicine.
PMID:19352025
Aegle marmelos commonly known as bael is a species of tree.
PMID:18830880
Scoparia dulcis A medicinal plant, dulcis. PMID:21905284
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) is used as a herb.
PMID:15026271
L-arginine (L-Arg) semiessential supplementation common natural
amino acid. PMID:16038634
Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort) PMID:18754092
Urtica dioica often called common nettle PMID:12834006
Usnea longissima, a medicinal lichen. PMID:16169175
Capparis decidua, a fruting tree also used in folk medicine and
herbalism. PMID:22272107
Indole-3-carbinol found at relatively high levels in cruciferous
vegetables such as broccoli
PMID:9512722, 14512388
Ascorbate Vitamin C. PMID:14512388
Sulforaphane It is obtained from cruciferous vegetables such as
broccoli. PMID:12628444, 18607771*, 22303412
Andrographis paniculata, may shorten the duration and lessen the
symptoms of common cold. PMID:11507728
Vitamin B-1 (thiamine) PMID:1132146, 10450194, 21308351*, 11514662*,
1270885
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) PMID: 5822598, 5550591, 1201246, 5794396,
237845, 3677785, 3582603, 12194936, 2721660, 1261528, 5721130,
14608016, 4400882, 7883462, 844948, 7337797, 5881,12641409, 4393763,
3497609, 16883966...(№
1244, OMIM.138300)
Vitamin B-6 (Pyridoxine) PMID:2721660, 3582603, 10450194, 15490422,
1270885, 7417521, 7337797, 7814235
Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) PMID: 844947, 1270885
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
(GOT) catalyzes the interconversion of aspartate an important enzyme
in amino acid metabolism. PMID:1132146, 10450194, 1253408
β-Carotene is a strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in
plants and fruits. PMID:19957244
3-Hydroxykynurenine (3OHKyn) a metabolite of tryptophan.
PMID:11273669
Ajoene ((E,Z)-4,5,9-trithiadodeca-1,6,11-triene 9-oxide), a
garlic-derived natural compound. PMID:9986706 PDB: 1BWC
Propolis a product made by bees. PMID:19394397
Resveratrol produced naturally by several plants PMID:12797471
No CiTO relationships defined:
http://vixra.org/abs/1506.0104
http://www.citeulike.org/user/emissrto/article/13645622
No CiTO relationships defined:
http://vixra.org/abs/1506.0104
http://www.citeulike.org/user/emissrto/article/13645622
No comments:
Post a Comment